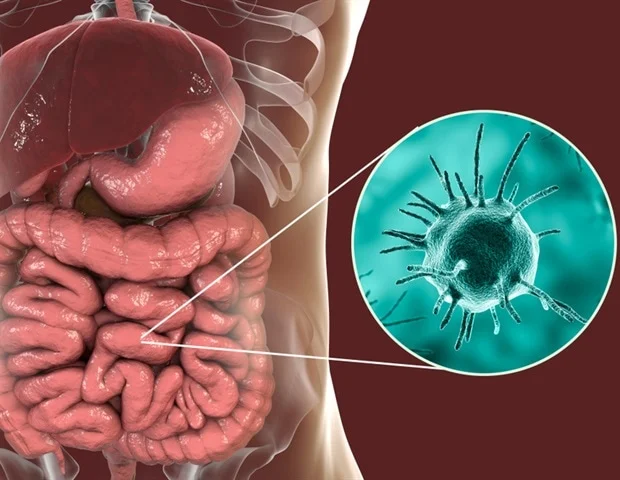
Intestinal amoebiasis is an infection caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. It primarily affects the large intestine and can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, loose stools, bloody diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and in severe cases, liver abscesses. Amoebiasis is more common in regions with limited access to clean water, inadequate sanitation, or poor hygiene practices. However, travelers, children, and individuals living in crowded or unsanitary environments can also be at risk. The good news is that intestinal amoebiasis is highly preventable when proper hygiene, food safety, and environmental precautions are followed.
This comprehensive guide explains effective ways to protect yourself from intestinal amoebiasis and reduce the likelihood of infection.
1. Practice Proper Hand Hygiene
One of the most important steps in preventing amoebiasis is consistent hand hygiene. Since E. histolytica spreads through the fecal-oral route, hands can easily become contaminated if proper washing is ignored.
Key practices
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and clean water for at least 20 seconds.
- Clean under fingernails, between fingers, and the backs of the hands.
- Always wash hands after using the toilet, changing diapers, cleaning up after pets, or handling soil.
- Wash hands before preparing meals, eating food, or handling drinking water containers.
- Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap and water are unavailable, but do not rely on them as the sole method of protection.
Proper hand hygiene significantly reduces the spread of cysts that could otherwise be accidentally ingested.
2. Consume Safe, Clean Drinking Water
Contaminated water is one of the most common sources of amoebiasis. If you are unsure about the safety of your water supply, take steps to disinfect it.
Methods to ensure safe drinking water
- Boiling: Bring water to a rolling boil for at least one minute (three minutes at higher altitudes).
- Filtration: Use high-quality water filters capable of removing protozoan parasites.
- Chemical disinfection: Chlorine tablets or iodine drops can help disinfect water when boiling is not possible.
- Bottled water: When traveling, choose sealed bottled water from reputable brands and avoid refilled containers.
Avoid drinking water from untreated sources such as rivers, lakes, or public taps in high-risk areas.
3. Practice Safe Food Handling and Eating Habits
Food contaminated with E. histolytica cysts is a major cause of infection. Food safety is especially important in regions with poor sanitation.
Food precautions
- Eat only thoroughly cooked foods, especially meats and seafood.
- Avoid raw fruits and vegetables unless you wash and peel them yourself using safe water.
- Avoid unpasteurized milk, cheese, and juices.
- Stay away from street food or vendors who do not follow visible hygiene practices.
- Make sure leftover food is reheated until piping hot.
- Keep raw foods separate from cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination.
Clean food preparation environments also reduce the transmission of parasites.
4. Improve Sanitation and Personal Cleanliness
Good hygiene and proper sanitation help prevent the spread of amoebiasis among households and communities.
Recommendations
- Use clean, functional toilets and avoid open defecation.
- Make sure toilet areas are disinfected regularly.
- Dispose of human waste properly, especially in areas without modern sewage systems.
- Clean bathroom surfaces with disinfectants.
- Avoid sharing towels, personal items, or utensils with people who may have a gastrointestinal infection.
These steps are essential, particularly in households with infants, elderly individuals, or anyone with compromised immunity.
5. Avoid High-Risk Behaviors
Certain lifestyle and sexual behaviors increase the risk of transmitting amoebiasis, as the infection can spread through oral-fecal contact.
Tips to reduce risks
- Practice safe sexual habits and avoid oral-anal contact.
- Use protective barriers when necessary.
- Ensure proper hygiene before and after intimate activities.
Being aware of how the parasite spreads can help prevent transmission in both personal and intimate settings.
6. Stay Informed When Traveling
Travelers to areas with poor sanitation are particularly vulnerable to amoebiasis. Understanding local risks and preparing accordingly is crucial.
Travel safety measures
- Bring portable water filters, bottled water, or purification tablets.
- Avoid ice cubes, as they may be made from contaminated water.
- Stick to well-cooked foods in reliable establishments.
- Carry oral rehydration salts in case of mild gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Learn basic phrases in the local language to inquire about water and food safety.
Taking preventive measures while traveling significantly minimizes exposure to infectious cysts.
7. Maintain a Clean Household Environment
Household contamination is a common route of transmission, especially if a family member is infected.
Actions to take
- Clean kitchen counters, cutting boards, and sinks regularly.
- Sanitize bathroom surfaces daily when someone shows symptoms.
- Ensure household water storage containers are kept clean and covered.
- Wash bedding and clothing of infected individuals separately and with hot water if possible.
A consistently clean environment reduces the chance of cysts lingering on surfaces and spreading.
8. Be Aware of Symptoms and Seek Medical Attention
Although prevention is the best strategy, early detection is also crucial. Amoebiasis can sometimes be asymptomatic, but typical symptoms include:
- Persistent diarrhea (sometimes with blood or mucus)
- Abdominal cramping or pain
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Gas or bloating
If symptoms persist, worsen, or include blood in stools, consult a medical professional for proper evaluation. Early diagnosis reduces complications and prevents transmission to others.
Note: In discussions involving antiparasitic medications, you may come across terms related to supply chains such as mebendazole wholesaler because mebendazole and similar drugs are commonly stocked and distributed globally. However, only a qualified healthcare professional can determine the right medication for amoebiasis or related conditions. Never self-medicate without proper diagnosis.
9. Strengthen Immunity Through a Healthy Lifestyle
A strong immune system can help the body resist infections and recover more quickly when exposed to pathogens.
Ways to support your immunity
- Eat nutrient-rich foods such as fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Drink adequate water daily.
- Get regular exercise.
- Manage stress effectively.
- Ensure proper sleep (7–9 hours for most adults).
While immunity alone cannot prevent amoebiasis, it helps your body stay resilient.
10. Community-Level Prevention
Preventing amoebiasis is not just an individual effort it also requires strong community sanitation practices.
Community improvements
- Construct reliable water supply systems.
- Improve sewage and waste management infrastructure.
- Provide public education about hygiene and sanitation.
- Support health campaigns aimed at parasite control.
Communities with better sanitation experience significantly reduced cases of amoebiasis.
Conclusion
Protecting yourself from intestinal amoebiasis involves a combination of personal hygiene, safe food and water practices, improved sanitation, and awareness of risks especially when traveling or living in high-risk environments. With the right habits, the infection is largely preventable. Staying informed, keeping your surroundings clean, and practicing good hygiene are the most effective ways to safeguard your health.











Leave a comment